Demystifying 3D Printing in On-Demand Manufacturing: A Comprehensive Guide to the Technology and Its Applications
In the realm of manufacturing, 3D printing has emerged as a revolutionary technology, transforming traditional production processes and opening new avenues for innovation. This blog aims to demystify 3D printing, particularly its applications in on-demand manufacturing, with a focus on the landscape in India. Whether you’re searching for “3D printing near me” or exploring custom 3D printing solutions, this comprehensive guide will shed light on the intricacies of the technology and its diverse applications.
Understanding 3D Printing
At its core, 3D printing, or additive manufacturing, builds objects layer by layer from digital models. This process allows for the creation of complex and intricate structures that traditional manufacturing methods may struggle to produce. The versatility of 3D printing lies in its ability to cater to diverse materials, including plastics, metals, ceramics, and more.
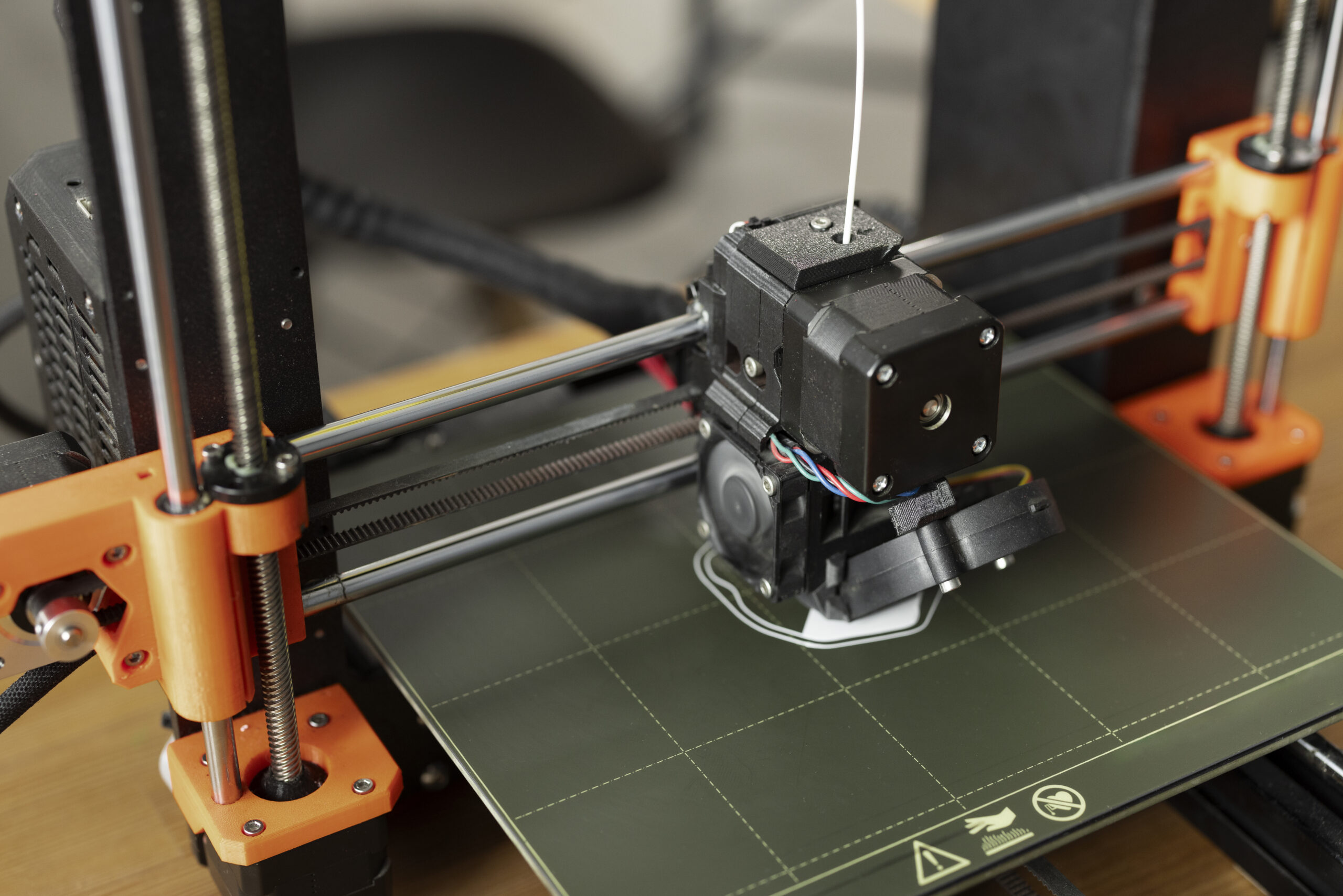

On-Demand 3D Printing Service
The advent of on-demand 3D printing services has significantly impacted the manufacturing landscape, providing businesses and individuals with a quick and efficient way to bring their ideas to life. By leveraging on-demand 3D printing solutions, users can turn concepts into tangible prototypes or end-use products with reduced lead times.
Custom 3D Printing Solutions
One of the key advantages of 3D printing is its customization capabilities. Traditional manufacturing often involves costly molds and tooling for each design iteration. In contrast, 3D printing enables the creation of bespoke, one-off products without incurring substantial setup costs. This makes it an ideal choice for those seeking custom 3D printing solutions tailored to their specific requirements.
Applications of 3D Printing in On-Demand Manufacturing
- Prototyping
Rapid prototyping is a hallmark application of 3D printing. Designers and engineers can quickly iterate and test their prototypes, accelerating product development cycles.
- Custom Parts Production
On-demand 3D printing services are ideal for producing low-volume, specialized components. This is particularly beneficial for industries requiring spare parts or unique components tailored to their equipment.
- Medical Models and Implants
The healthcare sector has embraced 3D printing for creating patient-specific models for surgical planning and producing customized implants, revolutionizing the field of personalized medicine.
- Jewelry and Fashion
Designers in the fashion and jewelry industries leverage 3D printing to produce intricate and personalized pieces, allowing for unparalleled creativity and precision.
- Aerospace and Automotive
3D printing is employed to fabricate lightweight and complex parts for aerospace and automotive applications, contributing to fuel efficiency and performance improvements.
The Intricate Process of 3D Printing in On-Demand Manufacturing
On-demand manufacturing has been revolutionized by the advent of 3D printing machining also known as additive manufacturing. This transformative technology has changed the traditional paradigms of production, offering unparalleled flexibility and efficiency. We delve into the step-by-step process of 3D printing in on-demand manufacturing.
- Digital Design
The journey begins with a digital design created using Computer-Aided Design (CAD) software. This 3D model serves as the blueprint for the physical object to be produced. Designers have the freedom to create intricate and complex structures that were once challenging or impossible with conventional manufacturing methods.
- File Preparation
Once the design is finalized, the CAD file undergoes preparation for the 3D printing process. This involves slicing the digital model into numerous thin layers. The slicing software generates a set of instructions for the 3D printer, detailing the path and specifications for each layer.
- Material Selection
The material used in 3D printing depends on the specific requirements of the project. Commonly, materials like resins, metals, plastics, ceramics and more, are chosen. The choice of material impacts the physical properties of the final product, such as strength, flexibility, and heat resistance.
- Printing Setup
Before the actual printing begins, the 3D printer must be calibrated and configured. This involves ensuring that the printing bed is leveled, the extruder temperature is set correctly, and the printing material is loaded. The printer follows the instructions from the sliced file to deposit layers of material in a precise and controlled manner.
- Layer-by-Layer Printing
The core principle of 3D printing is layer-by-layer construction. The printer adds material layer by layer, fusing each new layer to the previous one. This additive approach distinguishes 3D printing from subtractive manufacturing processes, where the material is removed to create the final shape.
- Support Structures (if needed)
In cases where the design includes overhangs or intricate features that may otherwise collapse during printing, support structures are added. These temporary structures provide stability during the printing process and can be removed later.
- Post-Processing
After the printing is complete, the object may undergo post-processing steps. This can include removing support structures, polishing, sanding, or applying additional coatings to enhance the final appearance and functionality of the product.
- Quality Control
Quality control in 3D printing is a crucial step to ensure that the printed object meets the desired specifications. This may involve dimensional accuracy checks, strength testing, and inspection of surface finish. Any deviations or defects are addressed to maintain the quality of the final product.
- Packaging and Delivery
Once the quality control checks are complete, the finished products are packaged and prepared for delivery. In the realm of on-demand manufacturing, this efficient process allows for quick turnaround times, enabling businesses and individuals to receive their custom 3D-printed items promptly.
To sum up
The 3D printing process in on-demand manufacturing is a sophisticated interplay of digital design, material science, and precision engineering. From the initial digital model to the final printed product, each step contributes to the creation of unique and customized items. As technology continues to advance, the world of on-demand 3D printing promises even greater possibilities, empowering industries and individuals to bring their ideas to life with unprecedented speed and flexibility. Embracing this technology opens doors to unparalleled customization, rapid prototyping, and a more sustainable approach to manufacturing. As the 3D printing landscape continues to evolve, it’s an exciting time for creators, innovators, and manufacturers alike.
Recent Post